Power electronics applications in industry sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with informal but serious style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Power electronics play a crucial role in modern industrial settings, from optimizing energy consumption to integrating renewable sources. Let’s delve into the realm of power electronics applications in industry and explore its impact on various sectors.
Power Electronics Fundamentals
Power electronics is a branch of electrical engineering that deals with the control and conversion of electric power. It involves the study and design of circuits that manipulate electrical power using semiconductor devices.
Power electronic devices are essential in various industrial applications to efficiently control the flow of electrical energy. Some common examples include:
Power Electronic Devices used in Industry
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs): Used for controlling high power loads such as electric motors and heaters.
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs): Commonly used in motor drives, uninterrupted power supplies (UPS), and renewable energy systems.
- Power Diodes: Essential in rectification circuits for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Power electronics play a crucial role in modern industrial applications due to their ability to efficiently convert and control electrical power. They enable precise regulation of voltage, current, and frequency, leading to improved energy efficiency, reduced losses, and increased system reliability.
Power Converters in Industrial Settings
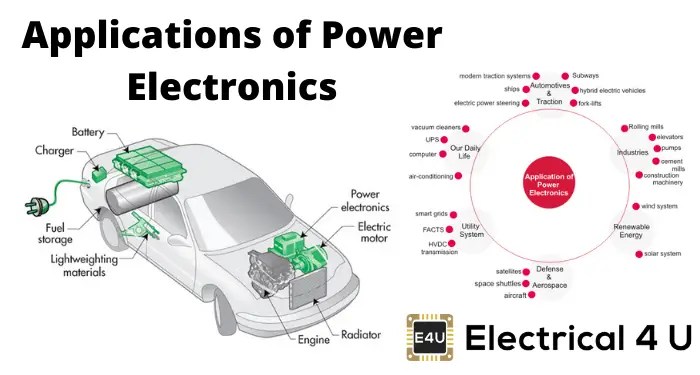
Industrial processes rely heavily on power converters to efficiently manage and control electrical energy. These devices play a crucial role in ensuring optimal energy consumption and maintaining reliable operations in various industries.
Types of Power Converters
In industrial settings, several types of power converters are commonly employed, including:
- AC/DC converters: These converters transform alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) to power various industrial equipment.
- DC/DC converters: Used to step up or step down DC voltage levels as needed for specific industrial applications.
- DC/AC inverters: Convert DC power into AC power, essential for running AC motors and other equipment in industrial processes.
- AC/AC converters: These converters change the voltage, frequency, or phase of AC power to meet the requirements of different industrial machinery.
Efficiency of Power Converter Topologies
Different power converter topologies vary in efficiency based on their design and operating conditions. For example:
- Buck converters are known for their high efficiency when stepping down voltage levels.
- Boost converters are efficient at increasing voltage levels, making them suitable for certain industrial applications.
- Multi-level converters can achieve high efficiency by reducing switching losses and improving voltage quality in industrial power systems.
Role in Optimizing Energy Consumption, Power electronics applications in industry
Power converters play a critical role in optimizing energy consumption in industries by:
- Regulating voltage and current levels to match the requirements of industrial equipment, minimizing energy wastage.
- Implementing power factor correction to improve the overall efficiency of industrial electrical systems.
- Enabling energy storage and management systems to make use of renewable energy sources effectively.
Motor Drives and Controls
Motor drives play a crucial role in industrial automation by enabling precise control over the speed, torque, and direction of motors used in various machinery and equipment. This level of control is essential for optimizing performance, increasing efficiency, and ensuring safe operation in industrial settings.
Power electronics are integral to motor speed control as they facilitate the conversion of electrical power to the appropriate form required to regulate the speed of motors. By adjusting the voltage, frequency, and waveform of the electrical signals supplied to the motor, power electronics devices such as inverters and converters can effectively modulate motor speed and performance.
Significance of Motor Drives in Industrial Automation
- Motor drives enable precise speed and torque control, allowing for efficient operation of machinery.
- They play a key role in automation processes by ensuring consistent and reliable performance of industrial equipment.
- Motor drives contribute to energy savings and reduced operational costs through optimized motor control.
Role of Power Electronics in Motor Speed Control
- Power electronics devices such as inverters and converters convert electrical power to the required form for controlling motor speed.
- By adjusting voltage, frequency, and waveform, power electronics regulate motor speed and torque efficiently.
- Advanced power electronics technologies enable precise and dynamic control over motor performance, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Examples of Industries Where Motor Drives Play a Critical Role
- Automotive Industry: Motor drives are essential for controlling the speed and position of robotic arms in manufacturing processes.
- Oil and Gas Sector: Motor drives are used in pumps and compressors for maintaining optimal operational conditions in drilling rigs and refineries.
- Food Processing Plants: Motor drives regulate conveyors, mixers, and other equipment to ensure efficient production and consistent product quality.
Renewable Energy Integration
Power electronics play a crucial role in enabling the integration of renewable energy sources in industrial setups. By efficiently converting and controlling the power generated from renewable sources, power electronics systems help industries harness the potential of solar, wind, hydro, and other sustainable energy forms.
Power Electronic Systems in Renewable Energy Applications
Power electronic systems used in renewable energy applications include:
- Grid-tied inverters: These devices convert the DC power generated by solar panels or wind turbines into AC power that can be fed back into the grid.
- Battery energy storage systems: Power converters control the charging and discharging of batteries to store excess energy generated from renewables for later use.
- Microgrid controllers: Power electronics manage the flow of power between renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and the main grid in microgrid applications.
Challenges and Opportunities of Integrating Renewables with Power Electronics in Industries
Integrating renewables with power electronics in industries presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Challenges:
- Intermittency: Renewable energy sources are often intermittent and unpredictable, requiring advanced power electronics systems to stabilize the energy output.
- Grid compatibility: Ensuring that power electronics systems comply with grid standards and regulations for seamless integration of renewable energy.
- Cost: Initial investment in power electronics equipment for renewable energy integration can be high, impacting the overall project economics.
- Opportunities:
- Energy independence: Integrating renewables with power electronics allows industries to reduce their dependence on traditional fossil fuels and benefit from clean, sustainable energy sources.
- Efficiency improvements: Power electronics enable optimal utilization of renewable energy, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings in industrial operations.
- Environmental impact: By embracing renewable energy integration with power electronics, industries can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Power Quality and Harmonics Mitigation: Power Electronics Applications In Industry
Power quality is crucial in industrial operations as it directly impacts the efficiency, reliability, and safety of electrical systems. Poor power quality can lead to equipment malfunction, increased downtime, and even damage to sensitive electronic devices. One of the major issues affecting power quality is harmonics, which are unwanted frequencies that distort the sinusoidal waveform of the power supply.
Power electronics play a significant role in mitigating harmonics and improving power quality in industrial settings. By using power electronic devices such as active filters, harmonic distortion can be reduced, ensuring a cleaner and more stable electrical supply. These devices actively monitor the system and inject corrective currents to cancel out the harmonic components, thereby improving the overall power quality.
Examples of Power Quality Issues and Solutions
- Power Factor Correction: In industrial settings, low power factor can lead to increased energy consumption and penalties from utilities. Power electronics can be employed to improve power factor by actively adjusting the reactive power, reducing losses and improving overall efficiency.
- Voltage Sags and Swells: Voltage fluctuations can cause equipment malfunction and reduce productivity. Power electronic devices such as voltage regulators and compensators can help mitigate these issues by stabilizing the voltage levels and ensuring a consistent supply to critical loads.
- Transient Overvoltages: Surges and transients can damage sensitive equipment and disrupt operations. Power electronics solutions like surge protectors and voltage suppressors can be used to limit the impact of transient overvoltages, protecting the equipment and maintaining system reliability.
Final Review
As we wrap up our exploration of power electronics applications in industry, it becomes evident that these technologies are reshaping the landscape of industrial operations. From enhancing power quality to driving efficiency, the future of industry lies in the realm of power electronics.
When it comes to ensuring safety in electrical systems, it is crucial to adhere to the electrical safety standards and regulations set in place. These guidelines help prevent accidents and ensure that electrical equipment is used properly to avoid any potential hazards.
Another important aspect to consider in power systems is electromagnetic compatibility in power systems. This ensures that different electrical devices can operate in the same environment without causing interference or malfunction, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable power system.