Lightning protection system design takes center stage in ensuring the safety of structures and equipment. Understanding the key components and standards is essential for effective protection against lightning strikes.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of lightning protection system design, we uncover the critical aspects that contribute to a robust and reliable system.
Lightning Protection System Basics
Lightning protection systems are crucial in safeguarding structures and individuals from the destructive power of lightning strikes. These systems are designed to intercept, conduct, and disperse lightning strikes in a safe manner.
When it comes to maintaining your car, there are some common mistakes that you should avoid to keep your vehicle running smoothly. From neglecting regular oil changes to ignoring strange noises, these errors can lead to costly repairs down the line.
To learn more about common car maintenance mistakes to avoid, check out this helpful guide: Common car maintenance mistakes to avoid.
Key Components of a Lightning Protection System
- Lightning Rods: These are metal rods placed at the highest points of a structure to attract lightning strikes.
- Conductors: Metal cables or rods that carry the lightning current from the rods to the grounding system.
- Grounding System: A network of conductors buried in the ground to safely disperse the lightning current.
- Surge Arresters: Devices that protect electrical systems from voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes.
Importance of Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is essential in a lightning protection system as it provides a path for the lightning current to safely dissipate into the ground. Without adequate grounding, the lightning strike can cause damage to the structure and its occupants.
Ensuring the safety of your vehicle is crucial, and understanding the top car safety features to look for can help give you peace of mind on the road. From advanced braking systems to blind spot monitoring, these features can help prevent accidents and protect you and your passengers.
To discover more about the top car safety features to look for, click on this informative link: Top car safety features to look for.
Risk Assessment and Site Evaluation
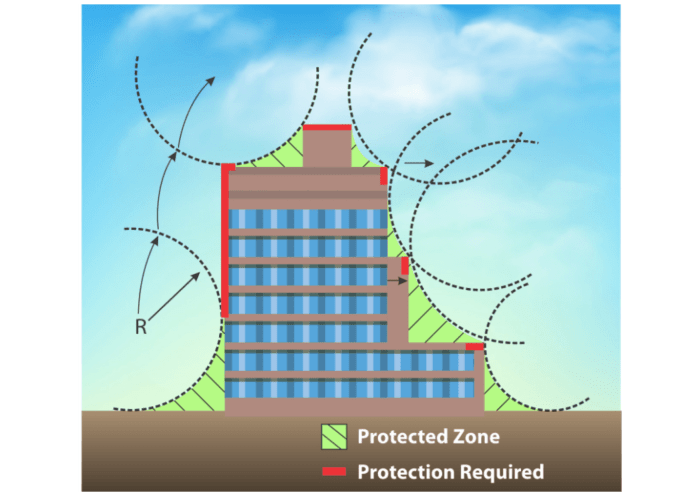
When designing a lightning protection system, it is crucial to begin with a thorough risk assessment and site evaluation to ensure the system effectively protects the structure and its occupants.
Risk Assessment Process
A risk assessment involves identifying potential hazards posed by lightning strikes to a particular structure. This includes considering the frequency of thunderstorms in the area, the height of the structure, the materials it is made of, and the consequences of a lightning strike. By analyzing these factors, engineers can determine the level of risk and the necessary level of protection.
Site Evaluation Impact, Lightning protection system design
Site evaluation plays a significant role in the design of a lightning protection system. Factors such as the shape and size of the structure, its location, and the presence of nearby trees or taller structures can impact the system’s effectiveness. For example, a tall building in an open area may require different protection measures compared to a smaller structure surrounded by taller trees.
Determining Protection Level
When determining the level of protection needed for a specific site, engineers must consider the structure’s occupancy, the value of the contents inside, and the importance of the structure itself. Critical facilities like hospitals or data centers may require a higher level of protection to prevent downtime and ensure the safety of occupants. Additionally, historical buildings or structures with unique architectural features may require specialized protection measures to preserve their integrity.
Design Standards and Regulations
When it comes to designing lightning protection systems, it is crucial to adhere to industry standards and regulations to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the system. Let’s dive into the various standards and regulations that govern the design and installation of lightning protection systems.
Relevant Industry Standards
- One of the key industry standards for designing lightning protection systems is NFPA 780 – Standard for the Installation of Lightning Protection Systems. This standard provides guidelines for the design, installation, inspection, and maintenance of lightning protection systems to mitigate the risk of damage from lightning strikes.
- Another important standard is IEC 62305 – Protection against lightning. This international standard covers the risk assessment, design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems, taking into account the specific characteristics of the structure or site.
Regulations for Installation
- In the United States, the installation of lightning protection systems is regulated by the National Electrical Code (NEC), specifically in Chapter 2 – Wiring and Protection. This code Artikels the requirements for the installation of lightning protection systems to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Many countries also have local building codes that govern the installation of lightning protection systems. These codes may vary depending on the region and must be followed to ensure the system’s effectiveness and safety.
Regional Design Approaches
- Design approaches for lightning protection systems may vary based on regional requirements and environmental conditions. For example, in areas prone to frequent lightning strikes, a more robust system with additional air terminals and grounding may be required to adequately protect the structure.
- Certain regions may have specific design considerations based on the type of structure, such as tall buildings, industrial facilities, or historic buildings. These considerations must be taken into account during the design phase to ensure the system meets the necessary safety standards.
System Design and Layout
When it comes to designing a lightning protection system layout, there are several key steps that need to be considered to ensure maximum efficiency and safety. The layout should be optimized to provide comprehensive coverage and protection against lightning strikes.
Selection of Materials for Effective Lightning Protection
To effectively protect a structure from lightning strikes, it is crucial to select the right materials for the lightning protection system. Conductors, air terminals, and grounding components should all be carefully chosen based on their conductivity, durability, and compatibility with the building structure. High-quality materials will ensure a reliable and long-lasting lightning protection system.
Optimizing the Design for Maximum Efficiency and Safety
In order to optimize the design of a lightning protection system, factors such as the height and location of air terminals, the placement of down conductors, and the grounding system must be carefully considered. By following industry standards and regulations, the design can be fine-tuned to maximize efficiency and safety, reducing the risk of damage caused by lightning strikes.
Surge Protection and Bonding
In a lightning protection system, surge protection devices play a crucial role in safeguarding against transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes. These devices help divert excessive electrical currents away from sensitive equipment and structures, preventing damage and ensuring system integrity. Proper bonding, on the other hand, is essential for creating a low impedance path for lightning currents to safely dissipate into the ground. Without effective bonding, the system’s overall effectiveness can be compromised.
Types of Surge Protection Strategies
- Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors (TVSS): These devices are commonly used to limit voltage spikes by diverting excess current to the ground. They are installed at key points in the system to protect against surges.
- Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs): GDTs are another type of surge protection device that provides fast response times to divert high energy surges away from sensitive equipment. They are often used in conjunction with TVSS for enhanced protection.
- Surge Protective Devices (SPDs): SPDs are designed to limit overvoltages and divert surge currents, protecting equipment and structures from damage. They are available in various configurations to suit different applications and voltage levels.
Final Summary: Lightning Protection System Design
In conclusion, a well-designed lightning protection system is paramount in safeguarding against the destructive power of lightning strikes. By adhering to proper design standards and regulations, optimal protection can be achieved for both people and property.