Electromagnetic compatibility standards are crucial for the seamless operation of electronic devices across various industries. From understanding the basics to exploring complex testing procedures, this topic delves into the intricate world of ensuring device safety and functionality.
Get ready to uncover the key aspects of electromagnetic compatibility standards and gain a deeper insight into why they are essential in today’s technological landscape.
Overview of Electromagnetic Compatibility Standards
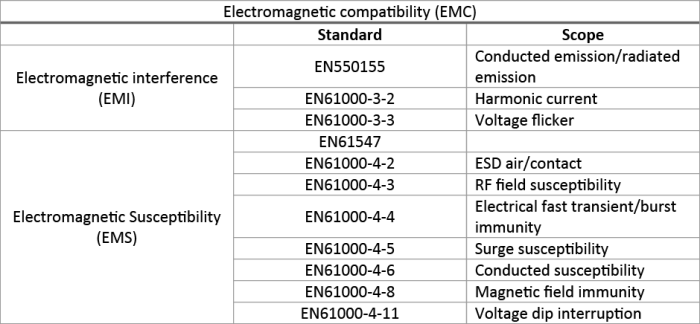
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standards are guidelines and regulations set in place to ensure that electronic devices can operate without interference in their electromagnetic environment. These standards aim to reduce electromagnetic interference between different devices and ensure that they do not generate excessive electromagnetic emissions.
Examples of Industries Adhering to EMC Standards
Industries such as telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics adhere to EMC standards to ensure that their products are safe, reliable, and perform as intended. Compliance with these standards is crucial to prevent malfunctions, data loss, and even potential safety hazards.
Importance of Complying with EMC Standards in Electronic Devices
- Ensures safety: Compliance with EMC standards helps prevent electromagnetic interference that could potentially lead to accidents or harm to users.
- Reliability: Adhering to EMC standards ensures that electronic devices perform consistently and reliably under various conditions.
- Legal requirements: Many countries have regulations mandating compliance with EMC standards to protect consumers and ensure fair market competition.
- Compatibility: By following EMC standards, manufacturers can ensure that their devices can coexist and operate effectively in the same electromagnetic environment.
Types of Electromagnetic Compatibility Standards
Conducted and radiated emissions standards play a crucial role in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility. Additionally, immunity standards are equally important to address the susceptibility of electronic devices to electromagnetic interference.
Conducted Emissions Standards
Conducted emissions standards focus on the electromagnetic interference generated through conductive paths such as power lines or signal cables. These standards specify limits on the amount of conducted emissions that electronic devices can produce, helping to minimize interference with other equipment.
Radiated Emissions Standards
Radiated emissions standards deal with the electromagnetic interference emitted by electronic devices in the form of radio frequency radiation. These standards define the acceptable levels of radiated emissions to prevent interference with nearby electronic devices or communication systems.
Immunity Standards
Immunity standards are designed to evaluate the ability of electronic devices to withstand electromagnetic interference without experiencing performance degradation. These standards ensure that devices can operate reliably in electromagnetic environments without being affected by external interference.
Examples of Specific Standards
– CISPR (International Special Committee on Radio Interference): CISPR standards cover a wide range of electromagnetic compatibility issues, including emissions and immunity requirements for various electronic devices.
– IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): The IEC sets international standards for the safety and performance of electrical systems, including electromagnetic compatibility requirements.
– FCC (Federal Communications Commission): The FCC in the United States establishes regulations and standards for electromagnetic compatibility to ensure the proper functioning of communication systems and electronic devices.
Compliance Testing Procedures
When it comes to ensuring electromagnetic compatibility of electronic devices, compliance testing procedures play a crucial role in determining if a device meets the required standards. These procedures involve rigorous testing to assess the device’s ability to function properly without causing interference to other devices.
Choosing the right products is key to achieving professional results in car detailing. Check out this car detailing products review to find the best products for your specific needs and budget.
Testing Environment and Equipment
Compliance testing is typically carried out in specialized laboratories equipped with instruments designed to generate electromagnetic fields and simulate real-world scenarios. The setup may include anechoic chambers to prevent external interference and ensure accurate testing results.
- EMI Receivers: Used to measure electromagnetic interference emitted by the device being tested.
- Spectrum Analyzers: Help in analyzing the frequency spectrum of the emissions and identifying any irregularities.
- Transient Generators: Used to simulate voltage spikes and transients that can occur in electronic systems.
Interpreting Results and Pass/Fail Criteria
Once the testing is complete, the results are carefully analyzed to determine if the device meets the specified electromagnetic compatibility standards. The criteria for pass/fail are usually based on limits set by regulatory bodies such as the FCC or CISPR. If the device’s emissions or immunity levels exceed these limits, it fails the compliance testing.
When it comes to keeping your car looking its best, knowing the right car waxing and polishing techniques is essential. From proper application to buffing, these tips will help you achieve a showroom shine.
Impact of Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) can have significant effects on electronic devices, causing disruptions in their normal operation. This interference can lead to malfunctions, data corruption, communication errors, and even device failure.
Effects of EMI on Electronic Devices
EMI can manifest in various ways, such as introducing noise in audio or video signals, disrupting wireless communications, causing errors in data transmission, and interfering with the functioning of sensitive electronic components. These effects can result in degraded performance, reduced reliability, and potential safety hazards.
- High-frequency interference can lead to signal distortion and loss of data integrity.
- Radiated EMI can affect nearby electronic devices, leading to cross-talk and interference issues.
- Conducted EMI can propagate through power lines and affect the operation of connected equipment.
Ways to Mitigate EMI through Proper Design and Shielding, Electromagnetic compatibility standards
Proper design practices and shielding techniques can help reduce the impact of EMI on electronic devices. Implementing the following measures can improve electromagnetic compatibility:
- Use of shielded cables and connectors to minimize the effects of radiated EMI.
- Grounding and bonding to reduce conducted EMI and provide a path for dissipation of unwanted currents.
- Isolation of sensitive components to prevent interference from affecting critical circuitry.
- Filtering and suppression of EMI at entry points to the device to block unwanted electromagnetic signals.
Proper shielding and grounding are essential to maintain the integrity of electronic systems in the presence of electromagnetic interference.
Real-World Scenarios Where EMI Caused Disruptions
In real-world scenarios, EMI can cause significant disruptions in various industries and applications. For example:
- In the healthcare sector, EMI from nearby equipment can interfere with the operation of medical devices, compromising patient safety.
- In automotive systems, EMI can disrupt communication networks within vehicles, leading to malfunctions in critical systems like engine control units.
- In industrial settings, EMI can cause errors in control systems, leading to production downtime and loss of productivity.
Global Harmonization of Standards
Global harmonization of electromagnetic compatibility standards is crucial for ensuring seamless operation of electronic devices across different regions of the world. By aligning standards, manufacturers can design products that meet the requirements of multiple markets, reducing the need for costly modifications and testing.
Efforts Towards Harmonization
Efforts towards harmonizing electromagnetic compatibility standards globally are led by organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These organizations work to develop common standards that are recognized and accepted worldwide, facilitating trade and interoperability of electronic products.
- The IEC plays a key role in developing international standards for electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring that devices meet the same technical requirements regardless of where they are used.
- The ISO focuses on harmonizing management systems standards, providing guidelines for organizations to implement processes that support EMC compliance.
Benefits and Challenges
Having uniform standards across different regions offers numerous benefits, including:
- Simplified market access for manufacturers, as products compliant with global standards can be sold in multiple countries without the need for additional testing.
- Enhanced consumer confidence, as products meeting international standards are perceived as safer and more reliable.
However, challenges in global harmonization of standards include:
- Differing regulatory requirements and enforcement mechanisms in various regions, leading to inconsistencies in compliance expectations.
- Resistance to change from established industry practices and national regulations, hindering the adoption of common standards.
International Organizations Working Towards Standardization
Several international organizations are actively involved in the standardization of electromagnetic compatibility requirements. These include:
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which develops standards for telecommunications equipment to ensure global interoperability.
- The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), which focuses on harmonizing standards for information and communication technologies in Europe and beyond.
Summary: Electromagnetic Compatibility Standards
In conclusion, the realm of electromagnetic compatibility standards is vast and vital, impacting the performance and reliability of electronic devices worldwide. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the necessary requirements for a smooth user experience.