Electromagnetic compatibility in power systems is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of electrical infrastructure. From understanding the sources of interference to implementing mitigation techniques, this topic delves into the intricate balance required to ensure seamless operation.
Exploring the challenges and regulations surrounding electromagnetic compatibility sheds light on the complexities involved in managing power systems effectively.
Overview of Electromagnetic Compatibility

Electromagnetic compatibility in power systems refers to the ability of different electronic devices and systems to operate in close proximity to each other without causing interference. This interference can manifest in the form of electromagnetic emissions or susceptibility, which can disrupt the normal functioning of these systems.
When it comes to restoring classic cars, it’s important to have the right tips and tricks up your sleeve. From sourcing parts to choosing the right tools, every step plays a crucial role in bringing a vintage beauty back to life.
If you’re looking for some classic car restoration tips, check out Classic car restoration tips for helpful insights.
Ensuring electromagnetic compatibility is crucial in power systems to maintain the reliability and efficiency of operations. Without proper compatibility measures, electromagnetic interference can lead to malfunctions, downtime, and even damage to equipment, posing serious risks to both the system itself and connected devices.
Importance of Ensuring Electromagnetic Compatibility
- Prevents operational malfunctions: By ensuring electromagnetic compatibility, power systems can prevent operational malfunctions caused by interference, leading to smoother and more reliable operations.
- Protects equipment: Compatibility measures protect equipment from damage due to electromagnetic interference, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
- Ensures safety: Electromagnetic compatibility helps maintain the safety of power systems by reducing the risks of unexpected failures or accidents caused by interference.
Challenges Associated with Electromagnetic Compatibility in Power Systems
- Increasing complexity of systems: As power systems become more complex with the integration of advanced technologies, ensuring electromagnetic compatibility becomes more challenging due to the proliferation of potential sources of interference.
- Interference from external sources: Power systems are vulnerable to electromagnetic interference from external sources such as radio frequencies, electromagnetic fields, and other nearby electronic devices, making it difficult to control and mitigate such interference.
- Compliance with regulations: Meeting regulatory standards for electromagnetic compatibility adds another layer of complexity, as power systems need to adhere to specific guidelines to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Sources of Electromagnetic Interference: Electromagnetic Compatibility In Power Systems

Electromagnetic interference (EMI) in power systems can originate from various sources, causing disruptions and malfunctions in electrical equipment. Understanding the common sources of EMI is crucial in mitigating its impact on power systems.
Power Lines and Switching Devices
Power lines and switching devices such as circuit breakers and relays can generate electromagnetic interference due to the rapid switching of currents. This can result in voltage spikes and harmonics that interfere with the normal operation of other devices connected to the power system.
Electronic Equipment
Electronic equipment like computers, televisions, and radios emit electromagnetic fields that can interfere with nearby power systems. The increasing use of electronic devices in homes and workplaces has contributed to the rise of EMI issues in power systems.
Lightning Strikes
Lightning strikes near power lines or substations can induce high levels of electromagnetic interference, leading to equipment damage and power outages. Lightning protection measures are essential to prevent EMI-related disruptions in power systems.
Electric Motors
Electric motors, particularly large industrial motors, can produce electromagnetic interference during operation. The varying magnetic fields generated by these motors can affect sensitive equipment in the vicinity, causing malfunctions and disturbances in the power system.
Arcing and Sparking
Arcing and sparking in power systems, often caused by loose connections or faulty equipment, can generate high-frequency electromagnetic interference. This can disrupt the normal functioning of electrical devices and lead to equipment failures if not addressed promptly.
Examples of Devices Causing EMI:
- Switching power supplies
- Variable frequency drives
- Fluorescent lighting
- Cell phones and wireless devices
Mitigation Techniques for Electromagnetic Compatibility
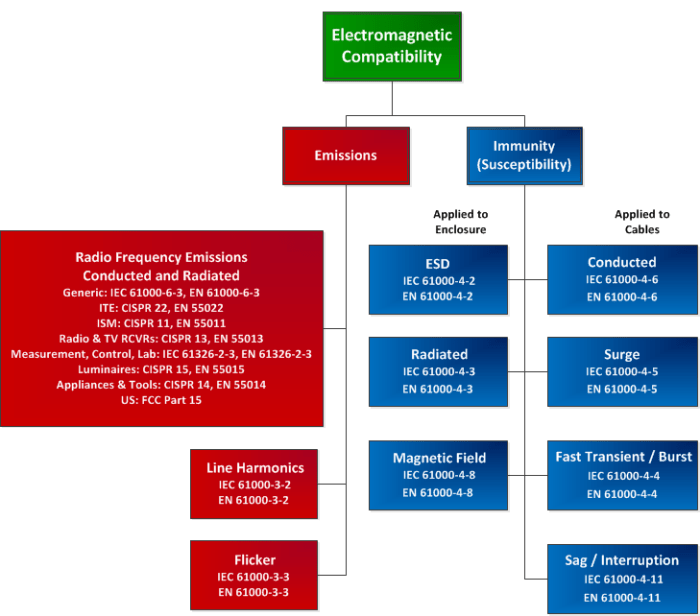
Electromagnetic interference can be a significant issue in power systems, affecting the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Various mitigation techniques are employed to minimize the impact of electromagnetic interference and ensure electromagnetic compatibility.
Passive Mitigation Strategies
Passive mitigation strategies involve the use of components or materials that absorb or filter out electromagnetic interference without requiring an external power source.
- Utilizing ferrite beads or chokes to suppress high-frequency noise.
- Implementing low-pass filters to attenuate high-frequency signals.
- Designing printed circuit boards with proper grounding and shielding techniques.
Active Mitigation Strategies
Active mitigation strategies involve the use of active electronic components to reduce or eliminate electromagnetic interference.
Looking to invest in a reliable car brand for 2021? With so many options out there, it can be overwhelming to choose the best one. To help you make an informed decision, check out the list of the Most reliable car brands 2021 for top-notch performance and durability.
- Employing active filters to cancel out unwanted noise signals.
- Using digital signal processing techniques to remove interference from power lines.
- Implementing adaptive interference cancellation algorithms to dynamically mitigate interference.
Role of Shielding
Shielding plays a crucial role in achieving electromagnetic compatibility by confining electromagnetic fields within a certain space and preventing them from interfering with sensitive electronic components.
Proper shielding design and material selection are essential to minimize electromagnetic interference.
- Employing conductive enclosures or encasing sensitive components in metal housings to contain electromagnetic emissions.
- Utilizing shielded cables and connectors to prevent external electromagnetic interference from affecting signal integrity.
- Ensuring proper grounding of shielding materials to provide an effective path for dissipation of electromagnetic energy.
Standards and Regulations
When it comes to electromagnetic compatibility in power systems, adherence to key standards and regulations is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of equipment and minimizing potential interference issues.
Key Standards and Regulations, Electromagnetic compatibility in power systems
- IEEE 519: This standard establishes limits for harmonic distortion in electrical power systems, helping to prevent excessive interference.
- CISPR 11: Focuses on emissions requirements for industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) equipment, ensuring that electromagnetic interference is kept at acceptable levels.
- IEC 61000 Series: These standards cover a wide range of topics related to electromagnetic compatibility, including immunity requirements for equipment operating in different environments.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with these standards and regulations is essential to guarantee that power systems operate efficiently and without disruptions. By following these guidelines, companies can ensure that their equipment meets industry requirements and performs reliably under various conditions.
Improving System Reliability
Adherence to regulations can significantly improve the overall reliability of power systems. By meeting the specified standards, companies can reduce the risk of equipment failures, minimize downtime, and enhance the safety of both the system and its operators.
Summary
In conclusion, electromagnetic compatibility in power systems is a multifaceted concept that demands attention to detail and adherence to standards. By addressing potential sources of interference and employing effective mitigation strategies, the reliability of power systems can be significantly enhanced, ensuring uninterrupted service and operational excellence.