Starting with Electric power distribution systems, this paragraph aims to give a captivating overview of the topic, highlighting the key components and challenges faced in modern power distribution networks.
Exploring different types of distribution systems, components, and the impact of renewable energy integration, this discussion delves into the intricacies of managing and optimizing electric power distribution systems.
Overview of Electric Power Distribution Systems
Electric power distribution systems play a crucial role in delivering electricity from power plants to consumers. These systems consist of various components that work together to ensure a reliable supply of electricity to homes, businesses, and industries.
Substations
Substations are key components of electric power distribution systems. They serve as points where high-voltage electricity from power plants is transformed into lower voltages suitable for distribution to consumers. Substations also help in regulating voltage levels and ensuring the efficient flow of electricity through the distribution network.
Transformers
Transformers are essential in the distribution system as they facilitate the transfer of electricity between different voltage levels. Step-down transformers reduce high-voltage electricity from power plants to lower voltages for distribution, while step-up transformers increase voltage levels for long-distance transmission. Transformers help in minimizing energy losses and ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of electricity to end-users.
Types of Electric Power Distribution Systems
Electric power distribution systems can be classified into different types based on their configuration and design. Let’s explore the main categories below:
Radial vs. Network Distribution Systems
Radial distribution systems are characterized by a single source of power feeding into multiple branches in a one-way flow. This design is simple and cost-effective but may result in power outages if there’s a fault in the main feeder. On the other hand, network distribution systems have interconnected loops that provide multiple paths for power flow. This redundancy enhances reliability but comes with a higher initial investment.
Overhead vs. Underground Distribution Systems
Overhead distribution systems use poles and wires to carry electricity above ground level. While this setup is easier and cheaper to install and maintain, it is susceptible to weather-related disruptions like storms and falling trees. In contrast, underground distribution systems bury cables beneath the surface, offering better aesthetics, improved reliability, and reduced environmental impact. However, underground installations are more expensive and challenging to repair.
Smart Grids in Modern Distribution Systems, Electric power distribution systems
Smart grids incorporate advanced communication and automation technologies to optimize the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power distribution. By integrating sensors, meters, and control devices, smart grids enable real-time monitoring, fault detection, and load management. This enhanced visibility and control empower utilities to better respond to changing energy demands, integrate renewable resources, and improve overall system resilience.
Components of Electric Power Distribution Systems
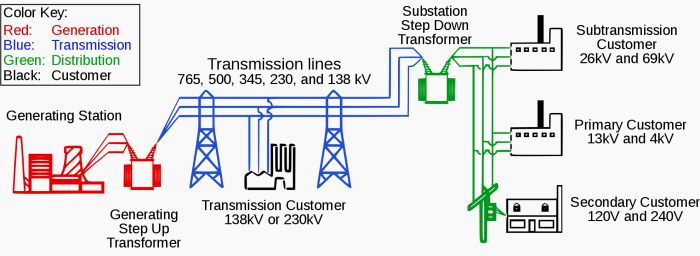
Electric power distribution systems consist of various components that work together to ensure the safe and efficient delivery of electricity to end-users. Three key components include distribution lines, distribution transformers, and protection devices.
Distribution Lines
Distribution lines play a crucial role in transmitting electricity from the substations to homes, businesses, and other end-users. These lines are typically overhead or underground cables that carry electricity at lower voltages compared to transmission lines. Distribution lines are responsible for distributing power to various points within a local area, ensuring a reliable supply of electricity to consumers.
Distribution Transformers
Distribution transformers are essential components in electric power distribution systems as they help reduce the voltage of electricity before it reaches end-users. These transformers step down the voltage from the distribution lines to a level that is safe for use in homes and businesses. By lowering the voltage, distribution transformers ensure that electrical appliances and devices operate safely and efficiently.
Protection Devices
Protection devices such as fuses and circuit breakers are critical for the safety and reliability of electric power distribution systems. Fuses are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in the event of a power surge or overload, preventing damage to electrical equipment and reducing the risk of fire. Circuit breakers serve a similar function by automatically shutting off the power supply when a fault is detected, protecting the system and preventing potential hazards.
Challenges and Solutions in Electric Power Distribution Systems
Electric power distribution systems face various challenges that can impact the reliability and efficiency of the system. Common challenges include power outages and overloads, which can disrupt the supply of electricity to consumers. To address these challenges, solutions such as automation and remote monitoring are being implemented to ensure efficient distribution of power.
Power Outages and Overloads
Power outages and overloads are major challenges in electric power distribution systems. Power outages can occur due to various reasons such as equipment failure, extreme weather conditions, or grid congestion. Overloads, on the other hand, happen when the demand for electricity exceeds the capacity of the system, leading to potential damage to equipment and disruptions in service.
- Implementing automated systems for real-time monitoring and control of the distribution network can help in early detection and mitigation of power outages.
- Introducing smart grid technologies that enable two-way communication between utilities and consumers can improve system reliability and response time to outages.
- Investing in grid modernization and upgrades to enhance the capacity and flexibility of the distribution system can prevent overloads and ensure a stable power supply.
Impact of Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power into traditional distribution systems poses new challenges and opportunities. While renewable energy offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based generation, it also introduces variability and intermittency in power generation.
- Developing advanced forecasting and scheduling tools to predict renewable energy output and optimize its integration into the grid can help manage the variability and ensure grid stability.
- Deploying energy storage systems such as batteries to store excess renewable energy and release it during times of high demand can enhance grid reliability and flexibility.
- Implementing demand response programs that incentivize consumers to adjust their electricity consumption based on renewable energy availability can help balance supply and demand on the grid.
Summary
In conclusion, Electric power distribution systems play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of electricity to end-users. By addressing challenges and embracing innovative solutions, the future of power distribution looks promising and sustainable.
When it comes to car maintenance, one of the crucial aspects to pay attention to is the lifespan of your car battery. By following simple tips like avoiding extreme temperatures and keeping it clean, you can extend the life of your battery and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding electromagnetic compatibility in power systems is essential to ensure the efficient functioning of electrical equipment. By implementing proper shielding and grounding techniques, you can minimize interference and maintain the reliability of your power systems.